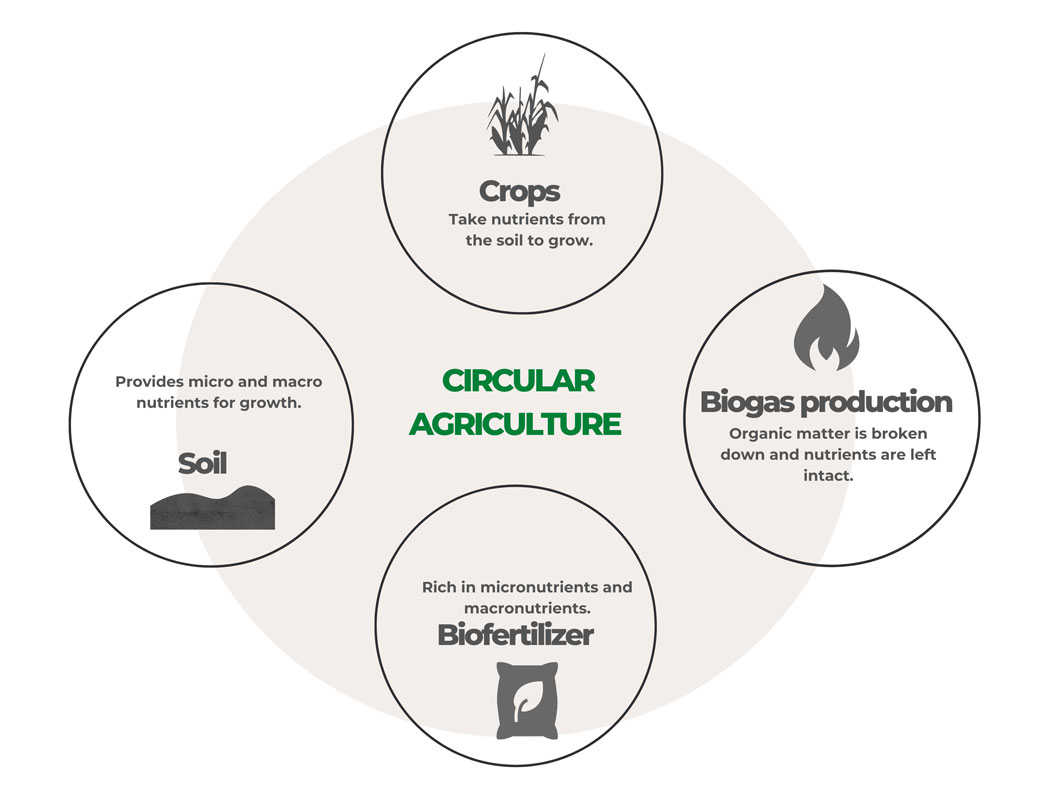
Environmental impact
Biomass is a renewable resource obtained from a natural source of energy: the sun. The electric plants that use biomass do not emit greenhouse gasses as they have a carbon dioxide closed cycle. There exist CO2 emissions during biomass harvesting, in the design of corn silos, in the motor generator, in the biofertilizer distribution and in the flare stack. Such emissions are reabsorbed as biomass grows, in this case corn, by means of photosynthesis.
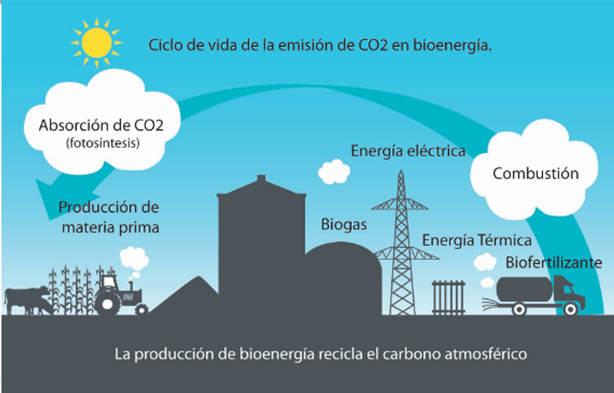
Circular agriculture
The digestate obtained as a by-product is a source of nutrients, like Nitrogen (N), Potassium (K), and Phosphorus (O), and plant hormones. These, used for irrigating the fields where corn was extracted, allow the return of nutrients to the soil, improving their catio-exchange capacity, extending the availability of nutrients, helping to keep the soil’s humidity and creating a microclimate for plants. This is why it is said that the process has a Closed Nutrient Cycle.